Sepsis
What is Sepsis?
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition triggered by the body’s response to an infection. When the immune system detects an infection, it mounts a powerful inflammatory response. In sepsis, this response is overwhelming and misdirected, attacking the body's own tissues and organs instead of just fighting the infection.
How Does It Happen?
Sepsis can arise from a wide range of infections, including those affecting the lungs, urinary tract, skin, or abdominal organs. However, it’s not the infection itself but rather the body’s disproportionate and dysfunctional response to the infection that leads to sepsis. This response can lead to a cascade of changes that can damage multiple organ systems, causing them to fail.
Why is Sepsis Dangerous?
If not recognized early and managed promptly, sepsis can lead to septic shock, a dramatic drop in blood pressure that can result in severe organ damage and death. The risk increases in people with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses, the very young, and the elderly.
The Project
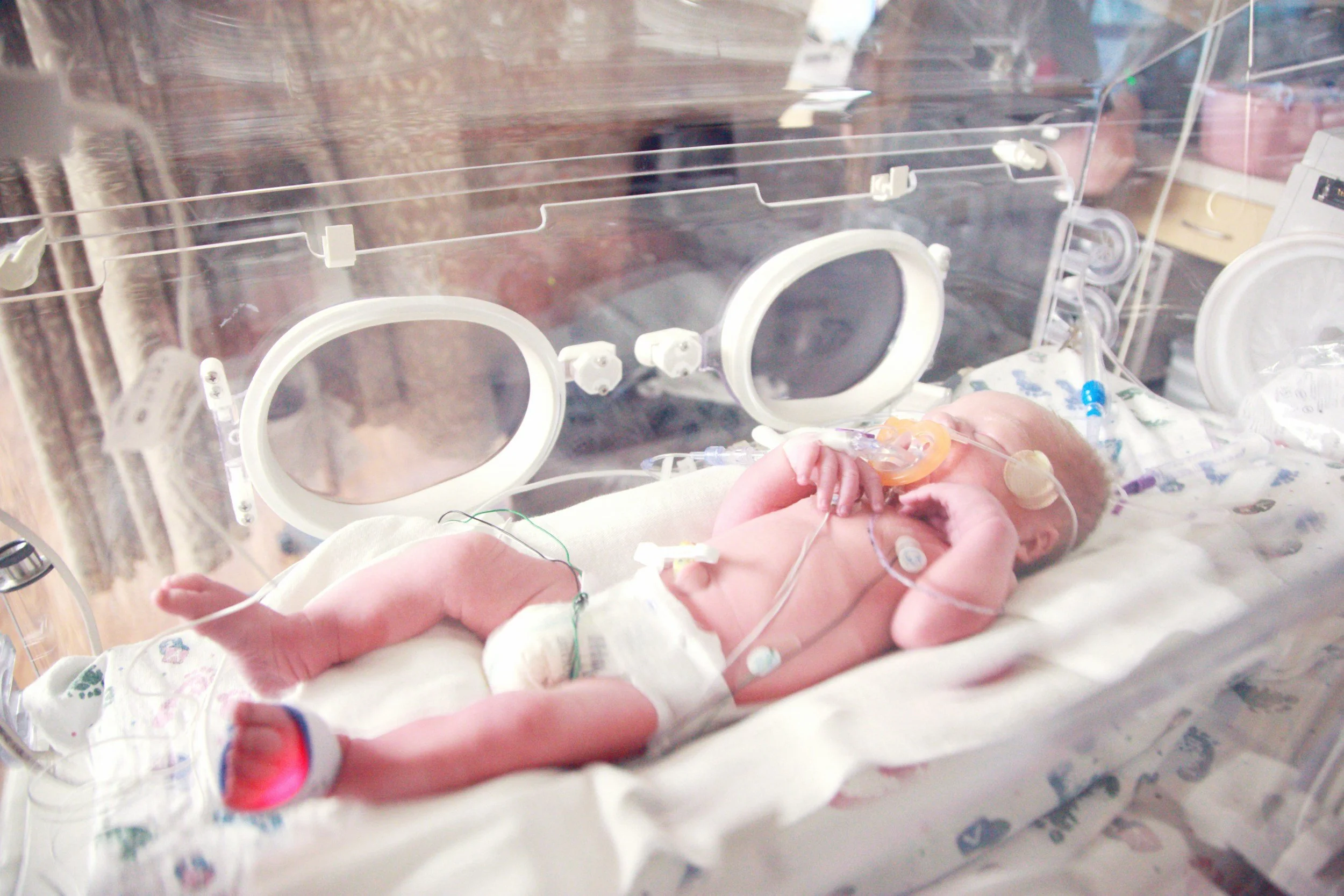
Accelerating Detection of Neonatal Sepsis (ADONIS) represents a groundbreaking initiative aimed at transforming the care of newborns through advanced machine learning technologies. In response to the global health challenge posed by neonatal sepsis, which affects over half a million newborns annually, ADONIS seeks to develop and deploy innovative diagnostic tools that ensure timely and accurate treatment decisions in neonatal intensive care units.
Objectives
Our primary objective is to enhance the outcomes for newborns by leveraging cutting-edge machine learning algorithms to:
Detect early signs of sepsis before clinical symptoms worsen.
Determine the optimal times for starting and stopping antibiotic treatments.
Decrease the unnecessary use of antibiotics, aligning treatment practices with precision health initiatives.
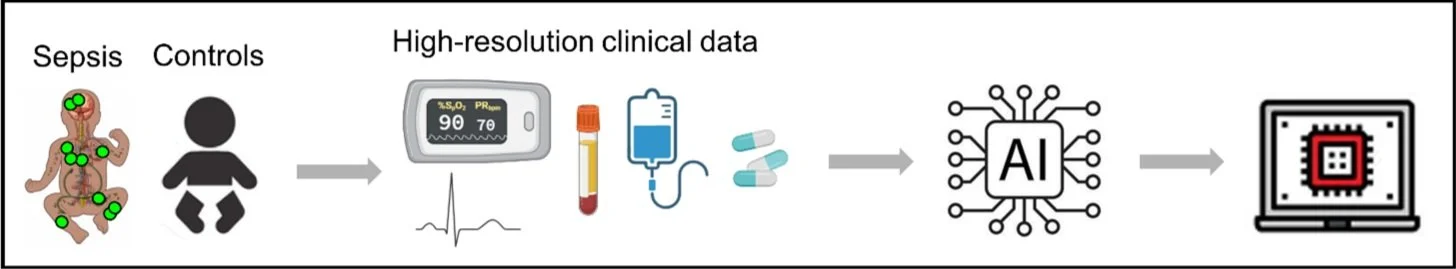
To achieve these goals, the ADONIS project employs a multi-faceted approach:
Data Collection: Gathering high-resolution data from over 10,000 neonatal cases and controls across multiple Swiss hospitals, focusing on detailed clinical and laboratory variables.
Model Development: Using state-of-the-art machine learning techniques to analyze patterns and predict sepsis from complex, multi-dimensional datasets.
Algorithm Validation: Testing and refining our predictive models across diverse clinical settings, both in Switzerland and internationally, to ensure reliability and accuracy.
Integration and Implementation: Designing a user-friendly digital tool that integrates seamlessly into existing clinical information systems for real-time, actionable insights.
Methodology
Expected Impact
The successful implementation of ADONIS will not only improve the survival rates and health outcomes of newborns but also set a new standard in the application of artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare. By reducing dependency on empirical treatments and enhancing the precision of neonatal care, ADONIS will lead to more sustainable healthcare practices and better resource utilization in hospitals worldwide.